A lot of times pharmaceutical labs create ceiling effects to avoid from children accidentally ingesting a toxic dose of that medication. That is the more you take the more pain relief you will get.
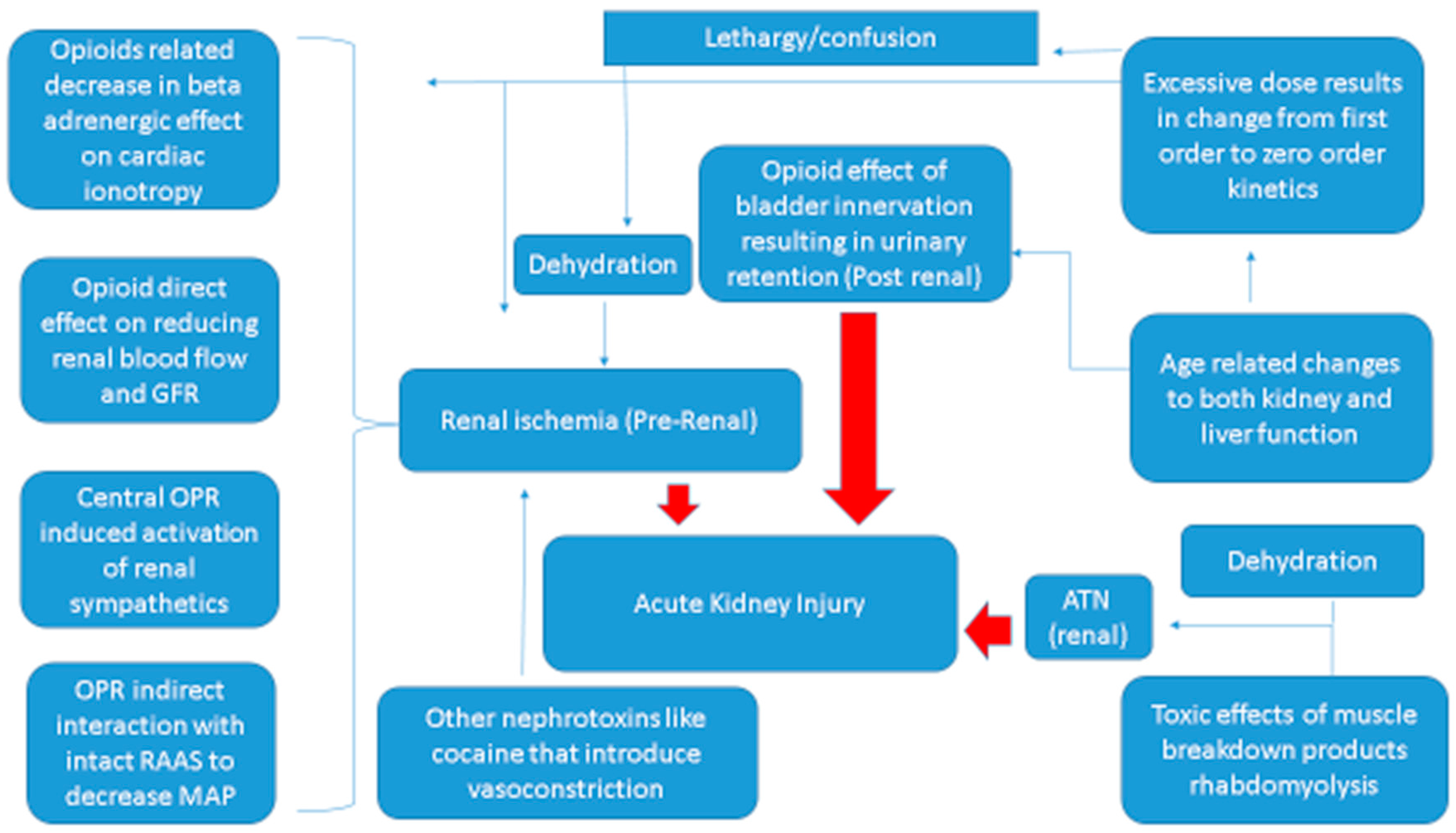
Ijms Free Full Text What Do We Know About Opioids And The Kidney Html
That is the reason why non-opioids are effective only for mild to moderate pain whereas opioids are useful for more severe pain intensity.

Ceiling effect opioids. The ceiling dose thing is because tramadol isnt what produces the opioid effects but rather its active metabolite o-desmethyltramadol does. Opioids have no true ceiling effect making them a suitable choice for patients with severe and escalating pain levels. This happens with many types of drugs including aspirin and opioids.
Note that naloxone has NOTHING to do with the effects of Suboxone. The therapeutic window of opioids is wide with no ceiling effect. In some fields biology physiology etc the ceiling effect refers to the point at which an independent variable no longer has an effect on a dependent variable when a kind of saturation has been reached eg the phenomenon in which a drug reaches its maximum effect so that increasing the drug dosage does not increase its effectiveness Baker 2004.
Full opioid receptor agonists eg morphine. Opioids on the other hand tend not to have a ceiling effect. In this video I explain why the ceiling effect is so important to the effects of buprenorphine for treating opiate dependence.
This is Part 3 Opioids Have Ceiling Effects High-Doses are Rarely Therapeutic and Another Hand-Crafted Graph I believed and was taught opioids had no intrinsic ceiling effect and didnt think there was much difference between someone being on 100 mg of morphine a day or 1000 mg. But the liver has a limit to how much tramadol it can metabolize into o-dsmt at a time which is what causes the ceiling effect. It has in essence hit a ceiling.
Buprenorphine causes limited respiratory depression with a ceiling effect at higher doses while fentanyl causes dose-dependent respiratory depression with apnoea at high dose levels. The ceiling effect describes the pharmacological phenomenon that once the therapeutic limit is reached an increase in dose will no longer increase the functional response but only the side effects. Author adminPosted on October 25 2011Categories Buprenorphine Education receptor actions SuboxoneTags ceiling effect heroin how suboxone works.
In conclusion buprenorphine is more favourable compared with fentanyl in respect to ventilatory control. Naloxone is a pure opioid antagonist that competes and displaces opioids from their receptor sites. There is no true analgesic ceiling effect for pure opioid agonists such as morphine hydromorphone or fentanyl.
4102019 This is Part 3 Opioids Have Ceiling Effects High-Doses are Rarely Therapeutic and Another Hand-Crafted Graph I believed and was taught opioids had no intrinsic ceiling effect and didnt think there was much difference between someone being on 100 mg of. At equipotent doses all opioids demonstrate a similar dose response. At this point taking higher doses does not increase its effect.
If combined with a pure opioid agonist these medications may precipitate acute pain and opioid withdrawal symptoms. The analgesic ceiling effect of a drug refers to the dose beyond which there is no additional analgesic effectThis concept often disregarded in the treatment of pain in the emergency department ED should be carefully considered when using common analgesics such as acetaminophen ibuprofen and opioids. Opioids play a fundamental role in pain management principally in the treatment of acute pain and cancer-related pain.
All clinically useful opioids are mu opioid receptor agonists. The drug ceiling effect refers to a particular phenomenon in pharmacology where a drugs impact on the body plateaus. For ibuprofen doses greater than 400mg do not provide further analgesia.
The Ceiling Effect and How it Works Suboxone when taken in low doses is an effective aid towards pacifying and allaying opioid withdrawal symptoms. Suboxone when used as directed accumulates within a persons bloodstream up to a point where it reaches maximum saturation in a persons bloodstream. The risk is however still elevated in the presence of benzodiazepines and other sedating.
In contrast nonopioids demonstrate a ceiling effect that generally is adequate for relief of mild to moderate pain pain relief rating of 45 in this scale. Buprenorphine due to its ceiling effect at the opioid receptor has a much lower likelihood of respiratory depression. Most AAs except corticosteroids have a narrow therapeutic window.
The higher the dose the more effect an opioid has on the feedback loop and the greater the risk of respiratory depression.

Medications For Chronic Pain Nonopioid Analgesics

Oral And Parenteral Opioid Analgesics Section 2 The Essence Of Analgesia And Analgesics
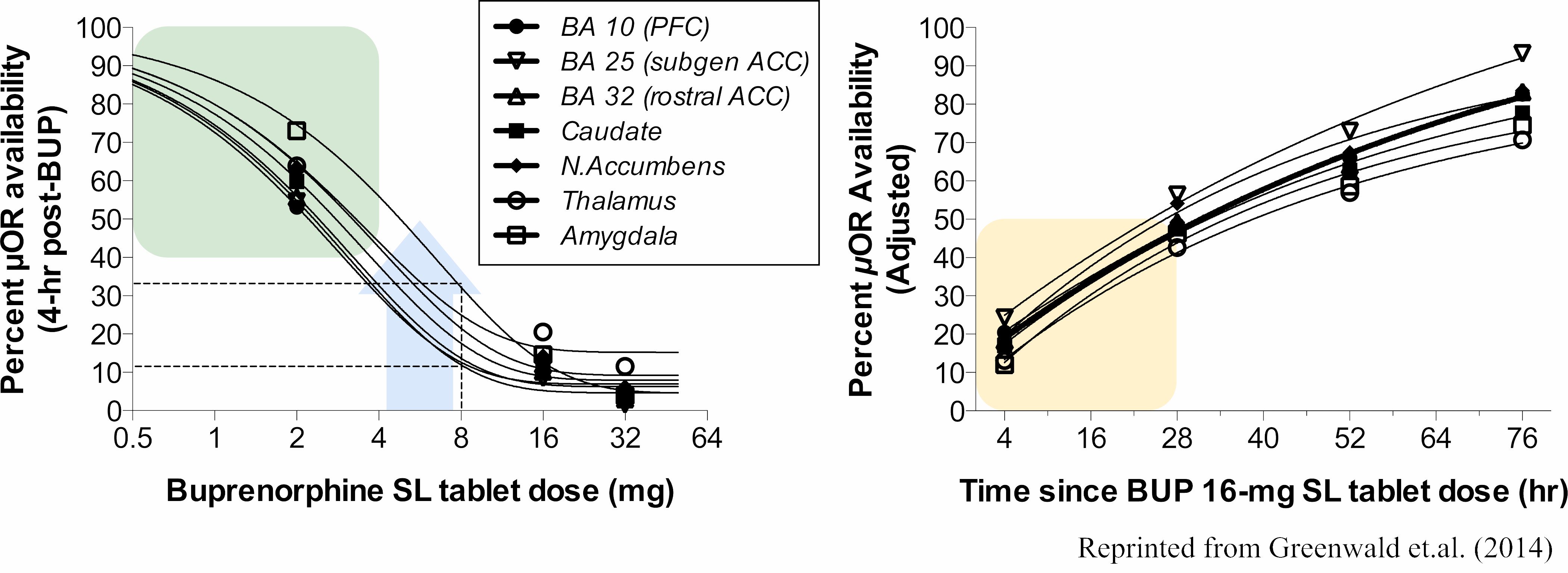
Special Issues For Patients With Suds Undergoing Surgery

Medications For Chronic Pain Nonopioid Analgesics

Qlik Capacity Whitepaper Letter Pdf Whitepaper Nclex Nurse
Https Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177 0310057x0503300104

Leo Buscaglia Water Ripples Ripple Kindness Projects

Methadone Vs Buprenorphine Similarities And Differences Hcrc

Pharmacology Of Opiates And Interactions With Other Depressants
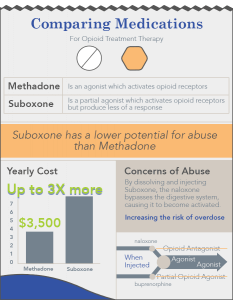
Suboxone Addiction And Abuse Treatments
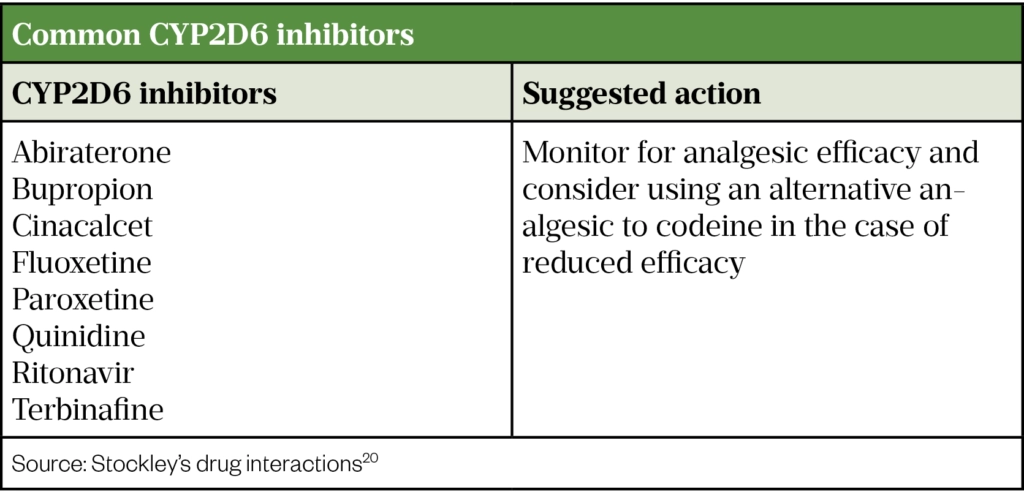
How Codeine Metabolism Affects Its Clinical Use The Pharmaceutical Journal

Oral And Parenteral Opioid Analgesics Section 2 The Essence Of Analgesia And Analgesics

Subutex Vs Suboxone What S The Difference Ask Our Doctors By Journeypure
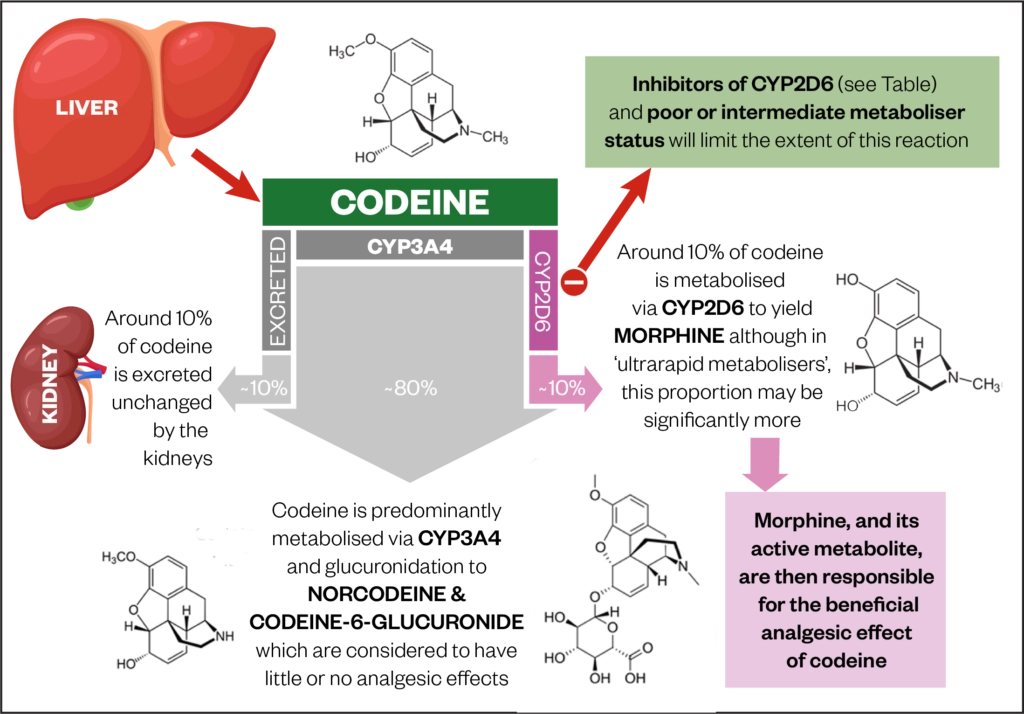
How Codeine Metabolism Affects Its Clinical Use The Pharmaceutical Journal




0 komentar:
Posting Komentar